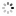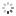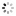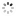Important Collectors Wristwatches, P...
Geneva, Mandarin Oriental Hotel Du Rhône, Nov 12, 2006
LOT 35
?Equation of Time ?Marchant? & Sidereal Time Deck Watch ? Patent Stromgren og Olsen? Alexandre Huning, Geneve, No. 54343, patent Stromgren og Olsen, No.541. Made circa 1920. Very fine and extremely rare, silver, keyless deck lever chronometer designed for astronomical navigation, with indications for Equation of Time and Sidereal Time as per Danish patent No. 22822 of 1918.
CHF 30,000 - 40,000
EUR 20,000 - 25,000 / USD 25,000 - 32,000
Sold: CHF 49,560
C. Four-body, ?bassine?, massive, polished. Hinged silver cuvette. D. White enamel with outer minutes and Equation of Time track with Arabic five minute numerals, subsidiary dials for the hours at 9 with radial Roman numerals, 24-Sidereal time hours dial at 3, seconds at 6. Gold hour, seconds and minute hand with sun terminal, blued steel ?Breguet? equation hand and ?spade? 24-hour hand. M. 45 mm., 20???, frosted gilt, 17 jewels, wolf?s tooth winding, straightline lever escapement, cut bimetallic compensation balance, blued steel Breguet balance spring, swan-neck micrometer regulator. Case stamped with Alexandre Huning?s trademark ?AH, Geneve?, dial signed ?Patent Stromgren og Olsen, No.541?. Diam. 60 mm.
| Grading System | |
|---|---|
Grade: |
|
Case: 3-9 |
Good Scratched |
Movement: 2 |
Very good |
Dial: 2-01 |
Very good HANDS Original |