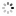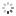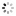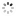Important Collectors Watches, Pocket ...
New York, Oct 17, 2008
LOT 286
Unique and Historically Important Longines, No. 4876616, case No. 66968. Made in 1930, presented to Professor Albert Einstein on February 16th, 1931 in Los Angeles. Fine, tonneau-shaped, 14K yellowgoldwristwatchwith a 14K yellow gold buckle. Accompanied by various photo-copies and photographs of Albert Einstein wearing the watch. Accompanied by various photocopies and photographs of Albert Einstein wearing the watch and a scan of a newspaper article.
USD 25,000 - 35,000
EUR 18,000 - 25,000 / CHF 28,000 - 40,000
Sold: USD 596,000
C. Two-body, solid, polished, hinged back engraved: Prof. Albert Einstein, Los Angeles, Feb. 16, 1931, lapidated lugs. D. Matte silver with luminous printed radial Arabic numerals, outer minute divisions, subsidiary seconds dial. Blued steel skeleton hands.M. Cal. 10.86 N, rhodium-plated, 17 jewels, straight-line lever escapement, cut bimetallic balance adjusted to temperatures and 2 positions, blued steel Breguet balance spring. Dial and movement signed, case signed AW (American Watch Co.). Dim. 25 x 40 mm. Thickness 10 mm.
| Grading System | |
|---|---|
Grade: |
|
Case: 3-8 |
Good Slightly scratched |
Movement: 3-6* |
Good Slightly oxidized Overhaul recommended, at buyer's expense |
Dial: 3-8-01 |
Good Slightly scratched HANDS Original |
Notes
Albert Einstein (1879 ?1955)
A theoretical physicist born at Ulm, inWürttemberg, Germany, who is best known for his theory of relativity and specifically mass? energy equivalence, E=MC2. In 1921 Einstein received the Nobel Prize in Physics for ?his services to Theoretical Physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect." Einstein's many contributions to physics include his special theory of relativity, which reconciled mechanics with electromagnetism, and his general theory of relativity, which extended the principle of relativity to non-uniform motion, creating a new theory of gravitation. His other contributions include relativistic cosmology, capillary action, critical opalescence, classical problems of statistical mechanics and their application to quantum theory, an explanation of the Brownian movement of molecules, atomic transition probabilities, the quantum theory of a monatomic gas, thermal properties of light with low radiation density (which laid the foundation for the photon theory), a theory of radiation including stimulated emission, the conception of a unified field theory, and the geometrization of physics. After schooling in Germany and Switzerland, in 1900 Einstein graduated from the Swiss Federal Polytechnic Institute in Zurich, intending to teach physics and mathematics. In 1902, after having failed to secure a teaching position, he began working as a technical assistant in the Swiss Patent Office in Bern. During this period he produced much of his remarkable work. In 1909 Einstein became a Professor at the University of Zurich and in 1911 Professor of Theoretical Physics at Prague, returning to Zurich in the following year to teach theoretical physics. In 1914 Einstein moved to Berlin, where he joined the faculty of the Prussian Academy of Sciences. When the First World War broke out, Einstein?s pacifist views led him to be considered a traitor by some. He and his wife and two sons went to live in Switzerland. When Hitler came to power in 1933, Einstein was in California. The Nazis considered him an enemy of the German state, and he decided to remain in America. That same year he accepted a position at the Institute for Advanced Studies in Princeton, New Jersey. In 1940 Einstein became a United States citizen. Einstein was active in Jewish causes, and near the end of his life he was offered the Presidency of the State of Israel. He declined, claiming that he had ?neither the natural ability nor the experience to deal properly with people and to exercise official functions." Shortly after Einstein's death in 1955, the 99th element was discovered and was called "Einsteinium" in his honor. A scientific and cultural icon, in 1999 Einstein was named "Person of the Century" by Time magazine. The name of Albert Einstein has become synonymous with genius. Literature: Nobel Lectures, Physics 1901-1921, Elsevier Publishing Company, Amsterdam, 1967.