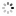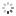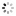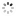Important Collectors' Wristwatches, P...
Geneva, Hotel Noga Hilton, Oct 16, 2005
LOT 194
?To Marshal Foch? Patek Philippe & Co., Geneve, No. 191653, case No. 286762. Made for Tiffany & Co., Switzerland, circa 1920. Very fine and rare, historically important 18K yellow gold cushion-shaped wristwatch with 18K yellow gold buckle. Presented to Marshal Foch by Alton T. Roberts and Franklin D?Olier, December 12, 192, for his 70th birthday.
CHF 20,000 - 25,000
EUR 13,000 - 16,000 / USD 16,000 - 20,000
Sold: CHF 27,600
C. Three-body, cushion-shaped, polished, straight down-turned lugs, the back inscribed ?Presented to Marshal Foch by Alton T. Roberts and Franklin D?Olier, December 12, 1921?. D. White enamel, radium coated Arabic numerals, outer minute track, subsidiary seconds. Radium coated blued steel ?skeleton? hands. M. 12???, rhodium plated, ?fausses cotes? decoration, 18 jewels, wolf?s tooth winding, straight line ?moustache? lever escapement, cut bimetallic compensation balance, blued steel Breguet balance spring, index regulator. Dial signed by Tiffany & Co., movement and case by Patek Philippe. Dim. 31 x 31 mm. Thickness 9 mm.
| Grading System | |
|---|---|
Grade: |
|
Case: 3-14 |
Good Damaged |
Movement: 3* |
Good Overhaul recommended, at buyer's expense |
Dial: 3-01 |
Good HANDS Original |