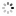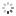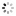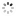Notes
Engraved on the case back: 'North Geomag Pole 87 - C.B.'The 'Explorer II' model, Ref. 1655, dates back to the 1970's and is called by collectors: 'The Steve Mc Queen watch'.Created for speleologists, the additional orange hand helps the user to distinguish the nocturnal from the diurnal hours.This model remained in the Rolex catalogues until 1982, then, from 1983 to 1988, the reference 16550 was availablewith white or black dial.The present watch was made in 1986. The explorer Carlo Bondavalli has a great use of the revolving graduated bezelin 24 hours, while at the Pole, the days last 24 hours.This watch was worn by Carlo Bondavalli, Explorer, who made an expedition in March-April 1987 to an unexploredterritory at the extreme north-east part of Groenland, at 1200 m. altitude, to report on scientific maps,' theGeomagnetic Pole', the cross-point of the terrestrial axis. Carlo Bondavalli decided to be the first to explore this land.In order to travel to a place where a normal compass is defective, Bondavalli invented his own system of orientation: asolar compass which, by a simple calculation of the day-hour and the position of the sun, allows the direction to bedetermined without having to use a complicated sextant.After a long and rough climb with a load of 40 kg, at temperatures of -59° C , and with a wind of 50 km/h., he finallyreached the geo-magnetic North Pole on April 9, 1987.The Bondavalli expedition gave the scientific world the benefit of information on the ecological future of the Arctic, aswell as biological research about tardigrades, microscopic organisms living in glacial territories.The geo-magnetic North Pole, is in the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, at 1900 km from the geographical North Pole. TheGeo-magnetic South Pole is in Austral Seas, 2600 km from the geographical South Pole. In 1957, the pole was on thecontinent, between this base and the Charcot station. It moves at about 10 km per year. These magnetic poles where amagnetic needle would be vertical, are nevertheless not at opposite extremes from each other: the straight line whichunites them therefore does not cross the center of the Earth. At the beginning of 1966, the geographical South Pole hasbeen moved of 45,7 cm., the co-ordinates or the Pole having been re-calculated by satellite GPS. The geomagnetic Polesor Poles of Gauss correspond to a terrestrial magnetic field without its irregularities where the 'aurora borealis' rise.They have been defined in 1839 by the German Astronomer, Mathematician and Physicist (1777-1855). They are closeenough to the magnetic Poles, but unlike them, they are directly opposite each other.Similar watches are published in 'Collezionare Orologi da Polso Rolex' New Edition by OSVALDO PATRIZZI, GUIDOMONDANI Editore Genova, pp. 260, 261 and 277.